Saral Diagnostics
·
25 Feb, 2023
·
Neurology
Saral Diagnostics
·
25 Feb, 2023
·
Neurology
Introduction
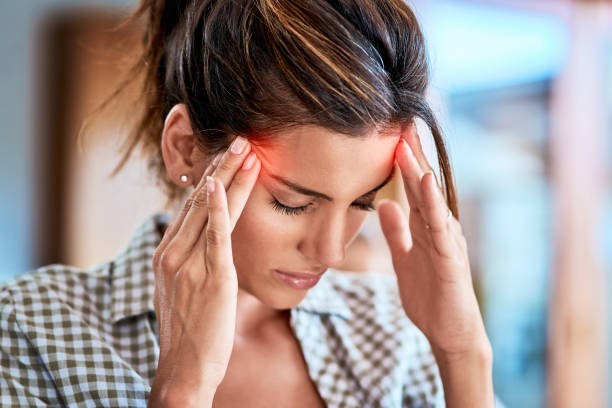
Headaches are one of the most common complaints in the world. They can range from a dull ache to a sharp, throbbing sensation. While some headaches can be managed at home with over-the-counter medications or other natural remedies, other times they might signal a more serious condition and require medical attention. In this blog, we will discuss the different types of headaches, what causes them, and how they can be treated.
What are Headaches
A headache is a common medical complaint characterized by pain in the head, neck, or face. Headaches can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, environmental triggers, muscle tension, and underlying medical conditions. Headaches can range in severity from mild to debilitating and can last anywhere from a few minutes to days or even weeks.
Types of Headaches
Headaches can be classified into two main categories: primary and secondary. Primary headaches are those that occur on their own, such as tension headaches, migraines, and cluster headaches. Secondary headaches are those that are caused by an underlying medical condition, such as sinus infections, head injuries, or brain tumors.
What’s the difference between a headache and a migraine
Headaches and migraines can be related, but there are some key differences between the two. A headache is a general term for any type of pain in the head or neck, while a migraine is a specific type of headache that is usually more intense and often includes other symptoms such as sensitivity to light and sound, nausea, and vomiting.
Who do headaches affect
Headaches can affect anyone, regardless of gender, age, or lifestyle. Some people are more prone to headaches than others, and certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing them. These factors include stress, lack of sleep, poor diet, hormonal changes, and certain medications.
What is the main cause of a headache
The exact cause of a headache can vary, depending on the type. Some primary headaches, such as tension headaches, are caused by muscle tension or stress, while others, such as migraines, are caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Secondary headaches can be caused by an underlying medical condition, such as a sinus infection or head injury.
Are headaches hereditary
Yes, some types of headaches can be hereditary. If a family member has a history of migraines or other types of headaches, it is possible that you may also be prone to them.
What headache symptoms require immediate medical care
Headache symptoms that require immediate medical attention include: severe, sudden, or worsening pain; pain that does not respond to over-the-counter medications; vision changes; confusion; difficulty speaking; weakness or paralysis; and fever.
How are headaches evaluated and diagnosed
If you experience any of the symptoms listed above or if your headaches are worsening or becoming more frequent, it is important to seek medical attention. Your healthcare provider will evaluate your symptoms and medical history to determine the cause of your headaches and the best course of treatment.
What tests will be done to diagnose headaches
Your healthcare provider may order a variety of tests to diagnose your headaches, including a physical exam, blood tests, imaging tests such as an MRI or CT scan, and a neurological exam.
How is a headache treated
The treatment for a headache will depend on the type and cause. Over-the-counter pain medications, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can be used to relieve mild to moderate headaches. Other treatments, such as rest, stress management, biofeedback, and medications, can be used to treat more severe headaches.
Stress management for headaches
Stress can be a major trigger for headaches and can make existing headaches worse. To manage stress, it is important to practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, yoga, and meditation. It is also important to get plenty of rest and to engage in physical activity to help reduce stress levels.
Bio-feedback for headaches
Biofeedback is a type of therapy that can help reduce the frequency and severity of headaches. It involves monitoring physical responses, such as heart rate and breathing, and then teaching the patient how to control these responses to manage pain.
Medications for headaches
Medications can be used to treat headaches, depending on the type and severity. Over-the-counter pain medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can be used to relieve mild to moderate headaches. Prescription medications, such as triptans and opioids, can be used to relieve more severe headaches.
Treating the underlying medical condition causing secondary headache
If a secondary headache is caused by an underlying medical condition, it is important to treat that condition to relieve the headache. This can involve taking medications, undergoing surgery, or making lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking or losing weight.
How can one get rid of a headache
The best way to get rid of a headache is to identify and avoid the triggers that cause it. This may involve making lifestyle changes, such as getting more rest, managing stress, and avoiding certain foods or activities. Over-the-counter pain medications can also be used to relieve mild to moderate headaches.
How can one prevent headaches
To prevent headaches, it is important to identify and avoid triggers, such as stress, lack of sleep, and certain foods. Other prevention strategies include getting regular exercise, managing stress, eating a healthy diet, and avoiding alcohol and caffeine.
Can headaches or migraines be cured
Headaches and migraines cannot be cured, but they can be managed through lifestyle changes, stress management, and medications. It is important to identify and avoid triggers and to talk to a healthcare provider about treatment options.
When should I see my healthcare provider about headaches
If your headaches are severe, frequent, or worsening, it is important to seek medical attention. You should also see a healthcare provider if your headaches are accompanied by other symptoms, such as confusion, vision changes, weakness or paralysis, or fever.