 Saral Diagnostics
·
28 Oct, 2022
·
Pathology
Saral Diagnostics
·
28 Oct, 2022
·
Pathology
FNAC is widely accepted as a screening test that has therapeutic implications. The sensitivity and specificity for FNAC of thyroid lesions show a wide variation of 65-98% and 72-100% specificity respectively.
Fine needle aspiration cytology has an estimated accuracy of approximately 94% for the diagnosis of PTC.
Role of FNAC is very vital in arriving at a presumptive diagnosis with subsequent cyto-histologic correlation. Whereas histopathological examination is gold standard for a definitive diagnosis, FNAC also provides high diagnostic value and it is still a cost-effective tool in the diagnosis of thyroid lesions as either benign, thereby reducing unnecessary surgery or malignant, requiring surgery. FNAC provides immediate results and is currently the preferred initial screening test for thyroid nodules. The Bethesda system classifies thyroid FNAC into six categories. Each category is linked to a malignancy risk and has a recommended clinical management.
BETHESDA SYSTEM FOR REPORTING THYROID CYTOPATHOLOGY

Papillary Thyroid carcinoma (PTC) is the most common type of thyroid malignancy with a better prognosis than that of other carcinomas.
Variants of PTC can prove to be a diagnostic challenge on FNAC. Some of these variants are associated with a poorer prognosis; therefore understanding of their cytomorphological features may expedite earlier diagnosis and management of the patient.
Oncocytic variant of PTC is a rare tumor with an incidence of 1-11% of all PTCs.
Oncocytic variant is often associated with local invasion and cervical lymph node metastases. According to many studies reported, it has been suggested that it has a higher recurrence rate as compared to classic PTC.
We reported a case of Oncocytic variant of PTC in a young female diagnosed on cytopathological features and was confirmed on histopathology.
Cytological features of Classic PTC have been extensively studied and well documented in the literature that include highly cellular smears, thin papillary fronds with fibrovascular cores and cellular swirls with nuclear crowding and overlapping, intranuclear grooves, intranuclear cytoplasmic inclusions and chewing gum colloid.
The features of oncocytic PTC on aspiration cytology have not been well described and PTC variants can pose diagnostic challenges on FNAC. Oncocytic variant of PTC on cytology shows papillary fronds. Cells show nuclear pleomorphism and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm as was present in our case. Many multinucleated giant cells are also noted.
Oncocytic variant can be differentiated from other oncocytic tumors by the presence of nuclear features of PTC.
Other tumors with oncocytic cells such as Hurthle cell adenoma, Hyalinizing trabecular adenoma and Oncocytic variant of Medullary carcinoma needs to be ruled out. In our case, we also gave a differential of Medullary carcinoma and advised S.calcitonin levels.
Another case of PTC, which was reported outside as Atypia of undetermined significance (AUS), Bethesda category III came to us for repeat USG guided FNAC and a diagnosis of Bethesda Category IV was rendered. A possibility of Follicular variant of PTC was also suggested. No true papillae were identified in our case. Syncytial clusters along with microfollicles were noted. Even in this case, hurthle cell change was noted but not as extensively as in our previous case along with few multinucleated giant cells. Excision was advised. Following this total thyroidectomy was done and the specimen was sent to our lab for histopathological examination. On histopathology, features were consistent with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma.
CASE 1– ONCOCYTIC VARIANT OF PTC
Cells are arranged in papillae with fibrovascular cores

Cells showing nuclear overlapping, bizarre giant cells seen

Cells showing marked nuclear pleomorphism, round to ovoid, central to eccentrically placed nuclei, powdery nuclear chromatin, moderate to abundant granular cytoplasm. Red arrow showing characteristic intranuclear cytoplasmic inclusions.

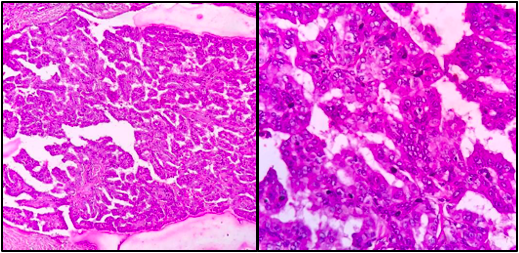
Excision Specimen- Microsections showing papillae

Oncocytes with optically clear nuclei & nuclear grooves

CASE-2
No true papillae identified

Total Thyroidectomy specimen

Finger like projections, cells lining the papillae show nuclear enlargement, nuclear membrane irregularity and chromatin clearing